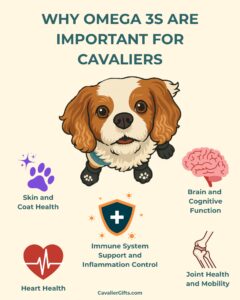
Health Benefits of Omega-3s for Cavaliers
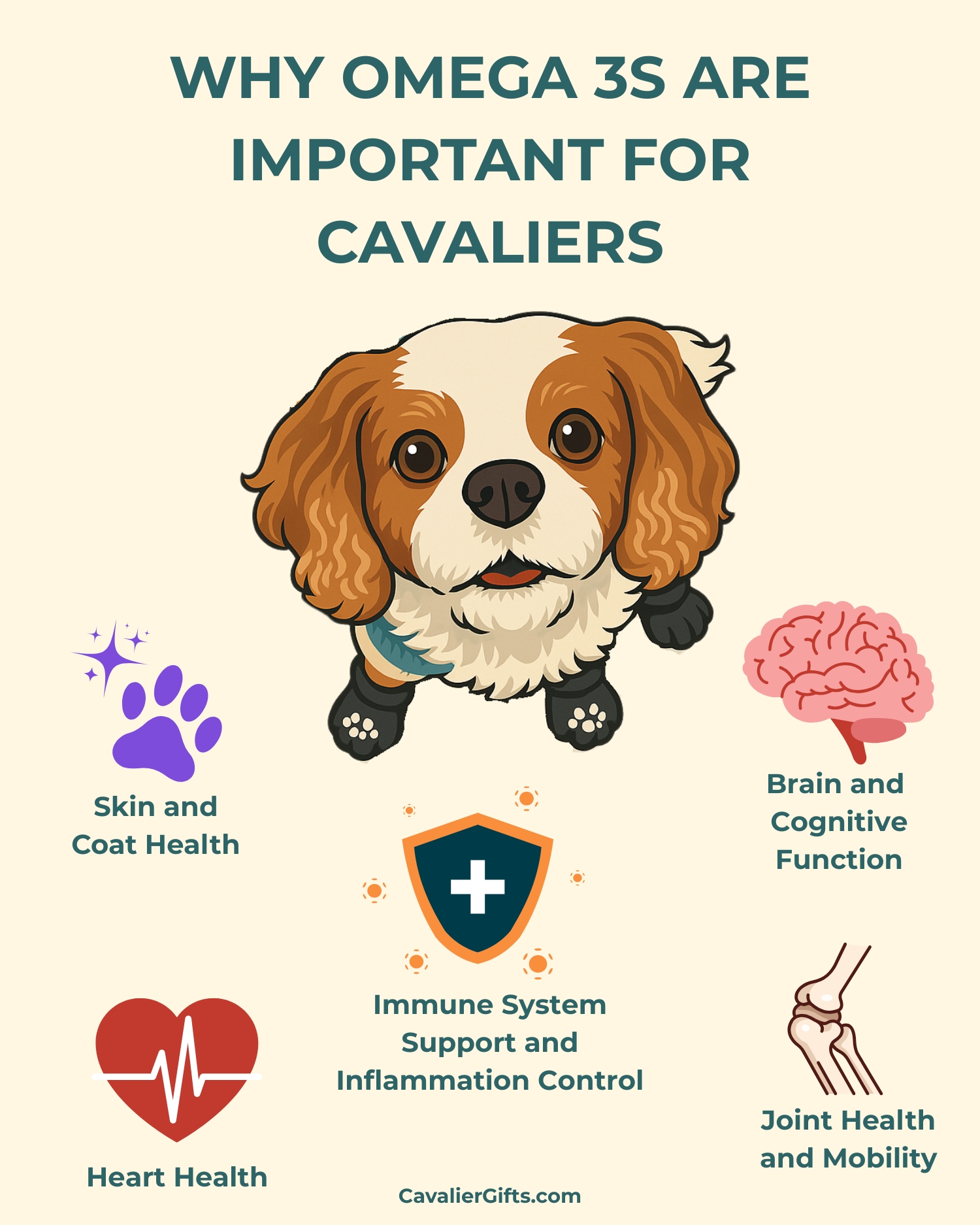
 Omega-3 fatty acids are one of the most important nutrients for Cavaliers, yet they’re often overlooked or misunderstood. These essential fats support heart health, brain function, joint mobility, skin condition, and even immune function. But not all omega-3 sources are created equal. Fresh fish, supplements, and plant-based options vary in effectiveness, and factors like oxidation and sourcing impact their quality. In this guide, I’ll break down the best omega-3 sources, how to choose high-quality options, and what to avoid to ensure your Cavalier King Charles Spaniel gets the maximum health benefits from their Omega-3s.
Omega-3 fatty acids are one of the most important nutrients for Cavaliers, yet they’re often overlooked or misunderstood. These essential fats support heart health, brain function, joint mobility, skin condition, and even immune function. But not all omega-3 sources are created equal. Fresh fish, supplements, and plant-based options vary in effectiveness, and factors like oxidation and sourcing impact their quality. In this guide, I’ll break down the best omega-3 sources, how to choose high-quality options, and what to avoid to ensure your Cavalier King Charles Spaniel gets the maximum health benefits from their Omega-3s.
Skin and Coat Health
Omega-3s help maintain a healthy skin, reducing dryness, flakiness, and itchiness. They also improve coat condition, making your Cavalier’s fur shinier and softer. Cavaliers, like many other breeds, can be prone to allergies and skin sensitivities, and omega-3s can help manage these issues by reducing inflammation in the skin.
Joint Health and Mobility
As Cavaliers age, they can develop arthritis and joint stiffness. Omega-3s have been shown to reduce inflammation in the joints, helping to alleviate pain and improve mobility. Dogs receiving sufficient omega-3s often experience less stiffness and better flexibility, which is particularly important for senior Cavalier King Charles Spaniels.

Brain and Cognitive Function
DHA is a crucial component of brain cell membranes and plays a significant role in cognitive function. In Cavalier puppies, it supports brain development and learning. In senior Cavaliers, it helps prevent cognitive decline and supports memory and problem-solving skills. Studies have shown that dogs supplemented with DHA perform better on cognitive tests than those that do not receive adequate amounts.
Heart Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for supporting cardiovascular function by helping regulate heart rhythm, reduce blood pressure, and improve circulation. For Cavaliers, who are especially prone to mitral valve disease (MVD), a common heart condition in the breed, omega-3s are even more important. Given their susceptibility to MVD, ensuring your Cavalier’s diet is rich in omega-3s can play a crucial role in supporting their heart health and may help slow the progression of the disease.
Immune System Support and Inflammation Control
Chronic inflammation is a factor in many health issues, including autoimmune conditions, allergies, and even cancer. For Cavaliers, who are prone to conditions like Chiari malformation, managing inflammation is especially critical. Omega 3s play an important role in regulating the body’s inflammatory response, helping to balance the immune system and reduce excessive inflammation. By incorporating omega 3s into your Cavalier’s diet, you can help protect against the inflammation that worsens conditions like Chiari malformation and support overall immune health.
Best Omega-3 Sources for Cavaliers
The best omega-3 sources for dogs are those that provide EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) in their most bioavailable forms. These two types of omega-3s are the most beneficial for dogs, as they are directly used by the body to support a variety of vital functions, from heart health to joint mobility. The most bioavailable forms of these omega-3s are typically found in marine-based sources, such as oily fish. Fish like salmon, sardines, mackerel, and anchovies are excellent options because they contain high levels of both EPA and DHA, making them ideal for supporting your Cavalier’s health. These fish provide omega-3s in a form that’s easy for the body to absorb, ensuring that your dog gets the maximum benefits.
In addition to fish, fish oil supplements can also be a great source of omega-3s. However, it’s important to choose high-quality, purified fish oils that are free of contaminants like mercury. If your Cavalier is sensitive to fish or you prefer plant-based sources, algae oil is another excellent option, as it provides DHA without the fishy aftertaste or concerns about ocean contaminants. While flaxseed and chia seeds offer plant-based omega-3s, they contain ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), which the body must convert into EPA and DHA, an inefficient process for dogs. This means that marine-based omega-3s are typically the best option for achieving optimal health benefits. By rotating between these high-quality sources, you can help ensure your Cavalier is getting the most effective omega-3s for their needs.
Watch our fresh fish DIY and don’t forget to subscribe to @CavalierTipsandFun for more!
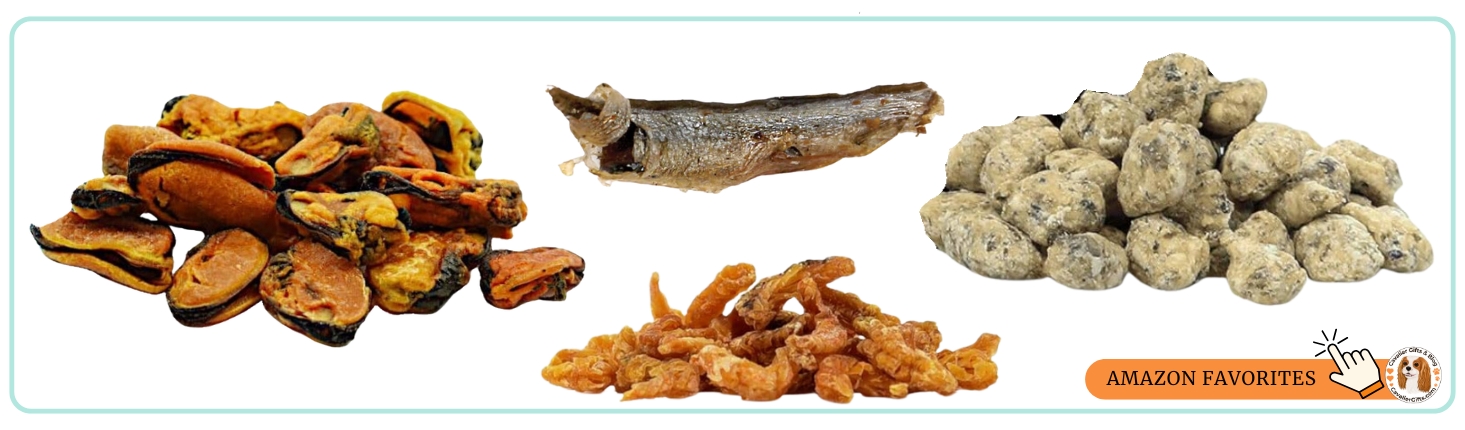
Fresh Fish (Whole Food Source of EPA and DHA)
Feeding fresh, oily fish is one of the most natural ways to provide omega-3s. However, choosing the right type of fish is essential due to concerns about mercury levels, sustainability, and proper sourcing.
Some of the best options for Cavaliers include:
- Sardines: Small, low-mercury fish that are naturally high in omega-3s. They are one of the safest whole-food sources.
- Anchovies: Similar to sardines, anchovies are rich in DHA and EPA while having minimal contamination risks.
- Herring: Often used in high-quality pet foods, herring is another small, oily fish packed with omega-3s.
- Atlantic Mackerel: This species is safe, but avoid king mackerel, which is high in mercury.
- Wild-Caught Salmon: A great source of omega-3s, but farmed salmon may contain higher levels of contaminants.
When feeding fresh fish, it’s important to either lightly cook the fish or feed it raw if it’s safely sourced. Cooking fish too much can break down some of the omega-3s, while raw fish (from a trusted, safe source) can provide the most nutrients. However, if you choose to feed raw fish, it should be frozen for a week first to reduce the risk of parasites, which can be a concern with certain types of fish.
It’s essential to avoid fish that have been prepared with added salt, spices, or sauces. These seasonings can be harmful to dogs. Also, always avoid feeding cooked bones, as they can splinter and cause serious internal injuries.
Fish Oil Supplements
Many pet parents turn to fish oil supplements to provide omega-3s, but not all fish oil supplements are the same. Choosing the right one for your Cavalier is important to ensure you’re giving them the best quality and the most effective nutrients.

How to Choose a High-Quality Fish Oil
When selecting a fish oil supplement, look for species-specific labeling. Instead of settling for generic “fish oil,” opt for oils like sardine oil, anchovy oil, or krill oil. This ensures transparency in sourcing and gives you a better idea of where the oil is coming from.
When choosing a fish oil supplement, it’s important to look at the levels of EPA and DHA, the two types of omega-3 fatty acids that provide the most health benefits for your dog. The label on the bottle should specify the amount of EPA and DHA in each serving, not just the total amount of fish oil.
For example, a bottle might say it contains 1,000 mg of fish oil per serving. But if the label doesn’t show how much of that is EPA and DHA, it’s hard to know how much of the oil is actually providing the beneficial omega-3s your dog needs.
Some fish oils may have more EPA, which is great for joint and heart health, while others may have more DHA, which supports brain function and reduces inflammation. Knowing exactly how much of each omega-3 is in the oil allows you to be more confident that you’re giving your Cavalier the right amount for their specific health needs. This way, you can make sure you’re getting the full benefits of the omega-3s in the supplement.
Also, choose products that are third-party tested. Reputable brands will test their oils for harmful contaminants like heavy metals, PCBs, and oxidation levels. This helps ensure the oil is safe for your dog and that it hasn’t been compromised during production.

Liquid vs. Capsules
Fish oil comes in two common forms: liquid and capsules. Liquid fish oil (often found in pump bottles) is convenient because it’s easy to dose, but it’s more prone to oxidation once opened. Oxidation occurs when the oil is exposed to light, heat, or air, so it must be stored in the refrigerator and used quickly to maintain its freshness.
On the other hand, capsules are more stable since the oil is protected from air exposure, which reduces the risk of oxidation. However, they can be harder to dose accurately, especially for small dogs.
Oxidation Risks
One of the biggest concerns with fish oil is oxidation. Omega-3s are very sensitive to light, heat, and oxygen, and when the oil oxidizes, it can lose its effectiveness and even become harmful. Signs of rancid fish oil include a strong fishy smell or an unusual taste.
To minimize the risk of oxidation, here are a few tips:
- Choose dark glass bottles instead of clear plastic, as glass helps protect the oil from light exposure.
- Store the fish oil in the refrigerator after opening to keep it fresh.
- Use the oil within 30 to 60 days of opening to ensure you’re getting the best quality.
By taking these steps to choose a high-quality fish oil and storing it properly, you can help ensure your Cavalier gets the full benefits of omega-3s for their heart, joints, and overall health.
Green-Lipped Mussels: A Powerhouse for Joint Support
Green-lipped mussels (Perna canaliculus), native to New Zealand, are one of the most beneficial natural sources of omega-3s for dogs. Unlike traditional fish-based omega-3 supplements that provide primarily EPA and DHA, green-lipped mussels contain a unique omega-3 fatty acid called ETA (Eicosatetraenoic Acid). ETA has been found to have additional anti-inflammatory properties, making it especially helpful for dogs suffering from joint issues like arthritis.
The anti-inflammatory effects of ETA, along with the presence of glucosamine and chondroitin, make green-lipped mussels an excellent option for promoting joint health. These compounds work together to support cartilage repair, reduce inflammation, and enhance mobility in dogs experiencing joint stiffness or discomfort. This combination is particularly beneficial for dog breeds, like Cavaliers, that are prone to developing joint issues as they age.
Comparing Omega-3 Content in Green-Lipped Mussels vs. Fish
In terms of EPA and DHA content, green-lipped mussels may not provide as high a concentration per serving as fatty fish, but their ETA provides an extra layer of anti-inflammatory benefits. This makes green-lipped mussels an excellent addition to a dog’s diet, particularly for those with joint concerns.
How to Feed Green-Lipped Mussels to Your Dog
Green-lipped mussels are often available as freeze-dried powder or in chewable treat forms. Both forms make it easy to incorporate them into your dog’s daily routine, but the powder can be sprinkled over food or mixed into homemade dog meals for ease of use.
As with any supplement, it’s important to start with a small amount to monitor how your dog responds, especially if they are new to green-lipped mussels or have a sensitive digestive system. For the dosing of green-lipped mussels, it’s always best to refer to the product-specific guidelines since the concentration can vary depending on the form (freeze-dried powder, chewables, etc.) and brand. However, a general recommendation often seen in supplements for dogs is:
- Start with 1/4 teaspoon per 10 pounds of body weight per day for powder form. This can be adjusted based on the dog’s response and their specific needs.

Plant-Based Omega-3s: Less Effective for Dogs, but Still Valuable
When it comes to omega-3 fatty acids, plant-based options are less efficient for dogs compared to animal sources like fish, as they primarily contain ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). While ALA is an essential omega-3 fatty acid for humans, dogs face challenges in converting ALA to the more bioavailable forms, EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are the forms most beneficial for their health. This makes plant-based omega-3s less effective for dogs in supporting the same health benefits as those derived from marine sources.
Why ALA Is Less Effective for Dogs
Dogs have a relatively inefficient ability to convert ALA into EPA and DHA. The process of conversion requires specific enzymes, which dogs do not produce in large enough quantities to convert sufficient ALA into the needed forms of omega-3s. As a result, while plant-based omega-3s can still offer some benefits, they are not as effective at delivering the omega-3s that support joint health, cognitive function, and heart health in the same way that fish-derived omega-3s do.
Nevertheless, plant-based sources of omega-3s are still valuable as part of a balanced diet. They can provide supplemental omega-3s and contribute to overall health but should not be relied on as the primary omega-3 source for dogs.
Common Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources
- Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds are one of the most popular plant-based sources of ALA omega-3s. They can be ground and added to your dog’s food. However, the conversion rate of ALA to EPA and DHA is low in dogs, so while flaxseeds may offer some benefits, they should not be relied on exclusively for omega-3 needs.
- Chia Seeds: Like flaxseeds, chia seeds are rich in ALA. These tiny seeds are highly nutritious and can be added to a dog’s meals. They can absorb water and form a gel, which can be helpful for digestive health. While chia seeds may offer some benefit, they should be seen as supplementary, not primary, sources of omega-3s for dogs.
- Hemp Seeds: Hemp seeds contain ALA as well, along with a well-balanced ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. While these can contribute to overall fatty acid intake in dogs, their conversion to EPA and DHA is also limited. Hemp oil, a more concentrated form, may be more effective but still not as efficient as fish oil or algae oil in providing the omega-3s dogs need for optimal health.
Algae Oil: The Better Plant-Based Alternative
While plant-based sources like flaxseeds and chia seeds are valuable in certain aspects, algae oil is usually a better plant-based option for dogs. Algae oil is derived from marine algae, which naturally produce DHA (and sometimes EPA) without requiring the conversion process. Unlike other plant-based sources that contain ALA, algae oil provides a direct source of DHA, the omega-3 that plays a critical role in brain function, heart health, and reducing inflammation.
Algae oil is especially beneficial for pet parents who prefer to avoid fish-based products for ethical, environmental, or allergy reasons. It provides the same essential omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil, but without the potential risks associated with mercury contamination or fish-based allergens. This makes algae oil a great plant-based alternative for ensuring your dog receives the health benefits of omega-3s.
Algae oil supplements are available in capsules or liquid form and can be incorporated into your dog’s diet just like fish oil. The recommended dosage varies by brand, so it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and consult your vet to ensure the right amount for your dog.
While algae oil is a great alternative to fish oil, there are a few differences to consider. One of the main differences is that fish oil generally contains more EPA, an omega-3 that is particularly helpful for reducing inflammation and supporting joint health, while algal oil tends to have more DHA, which is important for brain and eye health. Because of this, if your dog needs more EPA for inflammation or joint issues, fish oil might be a better choice. Additionally, algae oil can be more expensive than fish oil, and it may not be as widely available in stores. Another thing to note is that fish oil is often more bioavailable, meaning it’s easier for dogs to absorb and benefit from. That said, algae oil is still a very good option, especially if you’re looking for a more sustainable, vegetarian, or fish-free supplement. It’s always a good idea to talk to your vet about which type of omega-3 is best for your dog’s specific health needs.

How Much Omega-3 Does Your Cavalier Need?
For general health, the recommended omega-3 dosage, specifically EPA and DHA, is typically between 20 to 55 mg per pound of body weight per day. If your Cavalier has specific health issues, like arthritis or inflammation, the dosage may increase to 50 to 100 mg per pound. If your dog is lacking omega-3s, you might notice signs like dry skin, excessive shedding, joint stiffness, or a dull coat. To ensure you’re giving the right amount, it’s important to consult your vet, who can recommend the proper dosage based on your dog’s size and health concerns.
Final Thoughts
Omega 3s are essential for your Cavalier’s overall health, supporting heart, brain, joint and skin function. By incorporating a variety of high quality omega 3 sources such as fish, green lipped mussels and supplements, you can ensure your Cavalier King Charles Spaniel receives a well rounded intake of these beneficial fatty acids.
Quality matters, so focus on bioavailable forms of EPA and DHA, and always rotate the sources you use to prevent imbalances. Whether you opt for fresh fish, fish oil or green lipped mussels, it’s crucial to store and handle these sources properly to avoid oxidation.
Before making any changes, check with your veterinarian to tailor an omega 3 plan that best suits your Cavalier’s individual health needs. Consistently including omega 3s in their diet will support long term health and vitality, helping your dog thrive at every stage of life.
Do you feed your Cavalier fresh fish?
|
|
    
|
    
|
Google Ad Below